About Vue.js
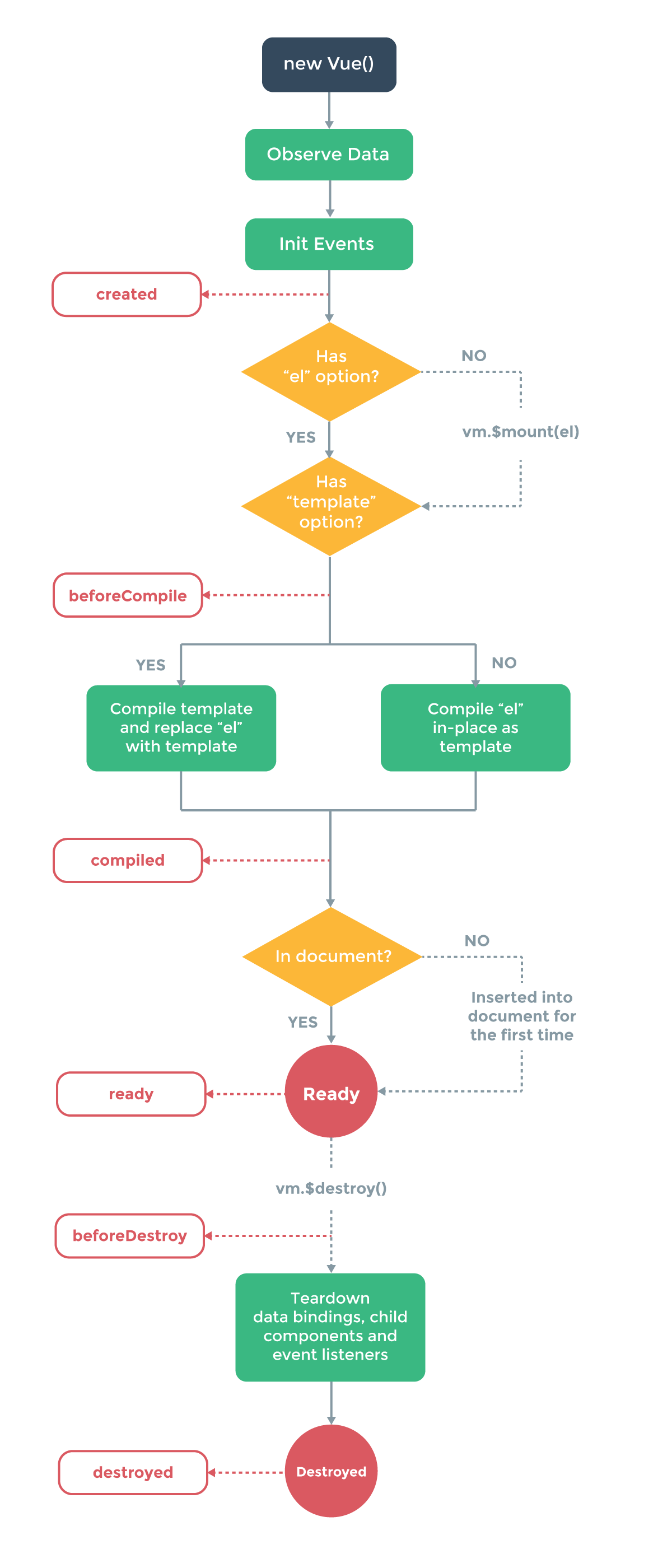
Vue.js is an open-source JavaScript framework for building user interfaces & single-page web applications. Vue.js is Inspired by the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern. It’s designed to help developers build better interactive interfaces while avoiding a steep learning curve, which means it’s a great choice for beginners and experienced web designers alike.
Vue js Interview Questions and Answers
Finally, Practice here the top Vue js Interview Questions for the best preparation of the Vue js Interview. These Interview Questions are very popular and are asked many times in Vue js Interviews. So, practice these questions to check your final preparation for your interview. apart from this, you can also download here Vue js Interview Questions PDF, completely free.