Explain Life cycle of Vue Instance.

Posted On: Jun 20, 2024
The Life cycle of each Vue instance goes through a series of initialization steps when it is created.
– for example, it needs to set up data observation, compile the template, and create the necessary data bindings. Along the way, it will also invoke some lifecycle hooks, which give us the opportunity to execute custom logic. For example, the created hook is called after the instance is created:
new Vue({
data: {
a: 1
},
created: function () {
// `this` points to the vm instance
console.log('a is: ' + this.a)
}
})
// => "a is: 1"
There are also other hooks which will be called at different stages of the instance’s lifecycle, for example compiled, ready and destroyed. All lifecycle hooks are called with their this context pointing to the Vue instance invoking it. Some users may have been wondering where the concept of “controllers” lives in the Vue.js world, and the answer is: there are no controllers in Vue.js. Your custom logic for a component would be split among these lifecycle hooks.
Lifecycle Diagram
Below diagram shows complete life cycle of Vue Instance
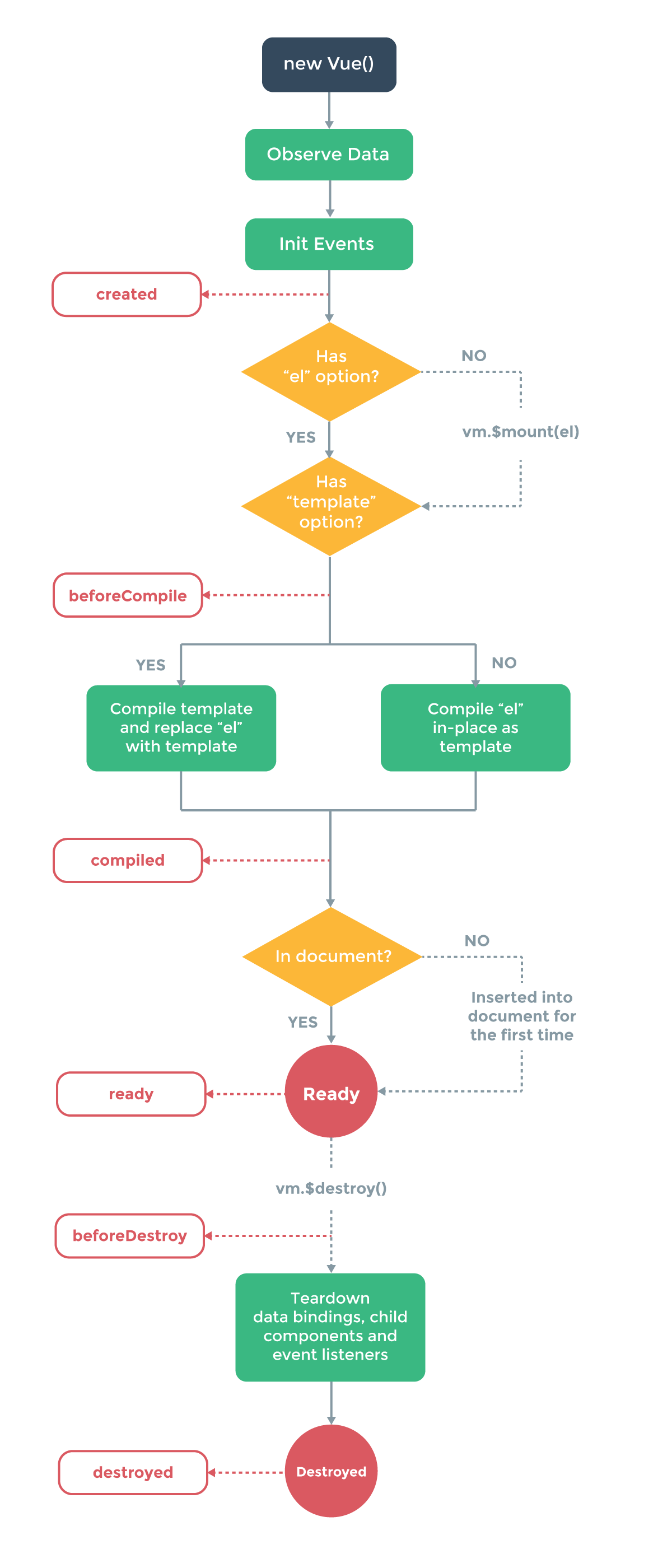
Source: https://v1.vuejs.org/guide/instance.html#Instance-Lifecycle
Also, Read React js Interview questions
Related Questions
Subscribe Our NewsLetter
Never Miss an Articles from us.
Recent Articles
Featured Categories
- Common Interview Questions
- Python Flask Interview Questions
- NoSQL Interview Questions
- jQuery Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- AngularJs Interview Questions
- Node JS Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Core Java Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- Laravel Interview Questions
- Wordpress Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
Vue.js Interview Questions
What is Vue.js?
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework that simplifies UI development. It offers reactive data binding, component-based architecture, and a flexible ecosystem. Vue's simplicity and versatility m..
Vue.js Interview Questions
List some features of Vue.js.
Vue.js offers templates for easy UI creation, reactive data binding, component-based architecture, built-in transitions for animations, and dynamic routing for single-page applications. These features..
Vue.js Interview Questions
How to create an instance of Vue js.
Creating a Vue.js instance involves specifying an HTML element for Vue to bind (el), defining reactive data properties, and adding methods for interactive functionality. This setup enables Vue.js to m..