Overview:
Before going to write the c program to check whether the number is Armstrong or not, let's understand what is Armstrong's number. Then, I will demonstrate the logic of Armstrong's number. After all, I will write the logic and C program to check if the number is Armstrong with output.
Table of contents:
- What is Armstrong's number?
- Demonstration for the logic of Armstrong's number
- The logic to check the number is Armstrong
- C program to check the number is Armstrong with output
- Conclusion
What is Armstrong's number?
Armstrong number is a number that is equal to the sum of cubes of its digits. For example 0, 1, 153, 370, 371 and 407 are the Armstrong numbers.
Demonstration for the logic of Armstrong number
A positive integer is called an Armstrong number (of order n) if,
abcd... = an + bn + cn + dn + ...
In the case of an Armstrong number of 3 digits, the sum of cubes of each digit is equal to the number itself.
First, we calculate the number of digits in our program and then compute the sum of individual digits raised to the power number of digits. If this sum equals the input number, then the number is an Armstrong number otherwise not.
Let's try to understand why 153 is an Armstrong number.
153 = (1*1*1)+(5*5*5)+(3*3*3) where: (1*1*1)=1 (5*5*5)=125 (3*3*3)=27 So: 1+125+27=153

Let's try to understand why 371 is an Armstrong number. 371 = (3*3*3)+(7*7*7)+(1*1*1) where: (3*3*3)=27 (7*7*7)=343 (1*1*1)=1 So: 27+343+1=371
The logic to check number is Armstrong
- Step 1: Take integer variable Arms
- Step 2: Assign value to the variable
- Step 3: Split all digits of Arms
- Step 4: Find the cube value of each digit
- Step 5: Add all cube-values together
- Step 6: Save the output to the Sum variable
- Step 7: If Sum equals to Arms print It is an Armstrong Number
- Step 8: If Sum not equal to Arms print It is Not an Armstrong Number
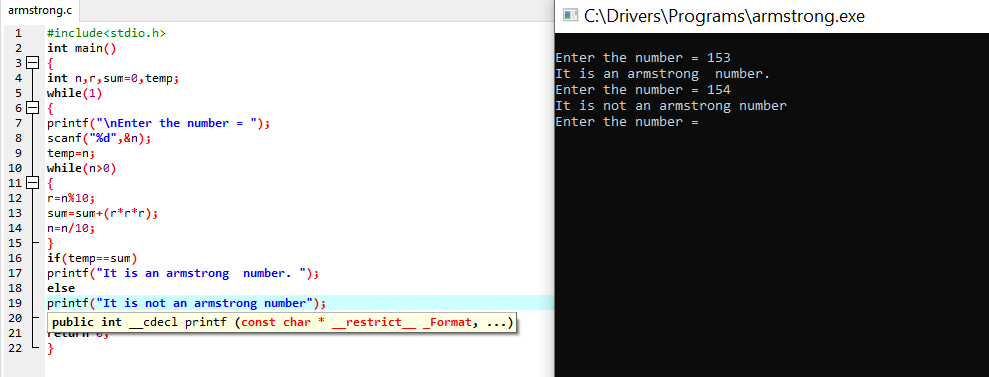
C program to check the number is Armstrong with output
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n,r,sum=0,temp;
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter the number = ");
scanf("%d",&n);
temp=n;
while(n>0)
{
r=n%10;
sum=sum+(r*r*r);
n=n/10;
}
if(temp==sum)
printf("It is an armstrong number. ");
else
printf("It is not an armstrong number");
}
return 0;
}
The output of the Program with code:
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
Enter an integer: 153
It is an armstrong number.
Conclusion:
In this program, the number of digits of an integer is calculated first and stored in n. And, the pow() function is used to compute the power of individual digits in each iteration of the second for loop.